
Olds Fibre Network
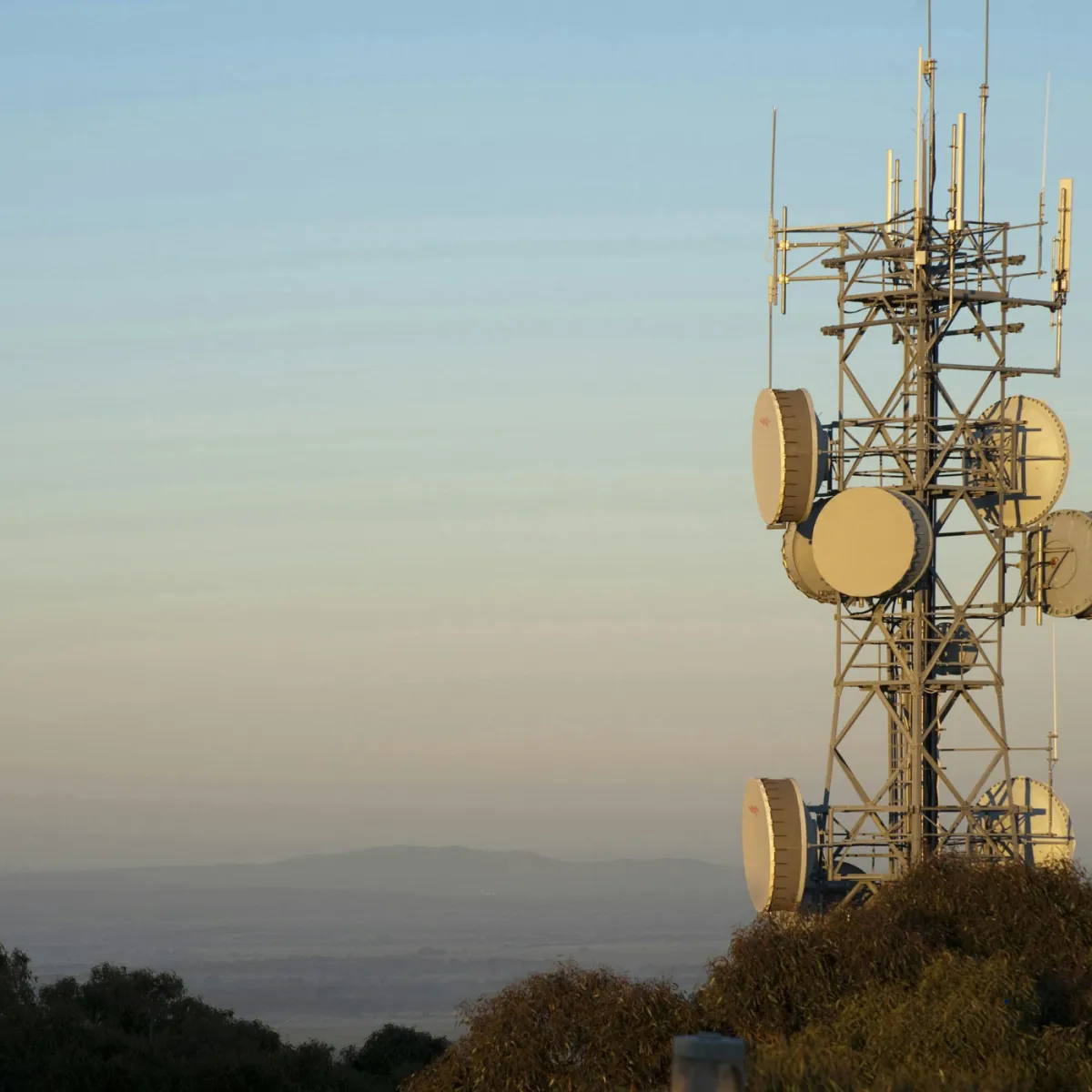

Location: Olds, Alberta
Partners:
Town of Olds, O-NET (a municipally-owned ISP), private contractors
Summary:
Olds built Canada’s first community-owned, open-access fibre optic network in a rural setting. This PPP involved the town collaborating with local businesses and private technology providers to deploy high-speed broadband.
Impact:
Enabled economic diversification, tech startups, remote education, and telemedicine in a town of fewer than 10,000 people.
Project:
Community-owned broadband infrastructure
Participants and Stakeholders:
Public Sector:
Town of Olds (Municipality)
Private Sector: O-NET (ISP arm of Olds Institute), private contractors
Civic Sector: Olds Institute for Community & Regional Development (a non-profit)
Leadership: Local municipal council, O-NET Board
Consulting Vendors: Technology integrators, fibre deployment consultants (not all publicly named)
Value Role Mapping:
Municipality: Infrastructure investment, policy
O-NET: Operations, service delivery
Institute: Strategic vision and funding coordination
Value Contributions:
Orchestration: Town of Olds
Operations: O-NET
Enablement: Olds Institute
Implementation: Contractors
Goal:
Deliver gigabit internet through a municipally owned, open-access broadband network
Roadmap & Results:
Discovery & Design-
Success Factor: 90%+ community support achieved via stakeholder engagement through Olds Institute
Planning & Configuration-
Funding Model: $13M total investment including public debt, private investment, and grants
Pilot & Build-
Result: Fibre-to-the-premises tested in business district; 40% uptake in pilot areas
Execution & Launch
Result: Town-wide broadband with symmetrical gigabit service
Governance & Scaling-
Result: Attracted tech startups and remote workers; improved real estate demand
Impact: Digital GDP growth est. 3.5–4% over 5 years (Olds Institute report)
Four value framework lenses:
B2B (Business-to-Business): Value created between private sector actors.
B2C (Business-to-Consumer): Value created from businesses or service providers to individual citizens.
G2B (Government-to-Business): Value delivered from public sector to business ecosystems.
G2C (Government-to-Citizen): Value delivered directly to citizens by government programs or PPPs.
B2B:
O-NET’s wholesale access enabled local ISPs and businesses to offer bundled services.
Contractors and technology vendors gained long-term operational contracts.
B2C:
Gigabit-speed internet for households improved access to streaming, telework, and e-learning.
G2B:
Local economic development via digital infrastructure attracted remote tech companies.
Municipal control allowed preferential service for local innovation hubs.
G2C:
Digital inclusion: elderly, students, and rural residents gained equitable internet access.
Affordable pricing through non-profit delivery model.
Value Framework Dimensions:
Economic Value (EV): Cost savings, revenue generation, asset optimization.
Functional Value (FV): Usability, access, infrastructure, reliability.
Experiential Value (XV): Citizen satisfaction, wellness, empowerment, trust.
Social or Public Value (SV): Equity, inclusion, environmental sustainability, capacity building.
Strategic or Ecosystem Value (ESV): Ecosystem enablement, innovation platform, new business models, systemic change.
Business Architecture
Flourishing Principles
Ecosystem
Optimization

Multi Stakeholder
Values

Global Flourish
CUSTOMER CARE
LEGAL
Copyright 2025. Global Flourish. All Rights Reserved.